Understanding Critical Thinking - Business Decision Making - ثاني ثانوي
Part 1
Chapter1: Identifying and Defining Problems
Chapter2: Solving the Problem
Chapter3: Thinking Critically
Chapter4: Group Decision Making and Problem Solving
Chapter5: Decision Support Tools
Chapter 6: Decision-Making Processes in Organizations
Chapter 7: Managing Teams to Support Decisions in Organizations
Chapter 8: Organizational Communication and Decision Making
Part 2
Chapter 9: Using Data to Support the Decision-making Process
Chapter 10: Decision Support System Fundamentals
Chapter 12: The Car Production Project
Chapter 13: The Ski Resort Project
Chapter 14: The Electric Car Project
Chapter 15: The Airline Project
Chapter 3 Thinking Critically Suppose as part of the Saudi Vision 2030 initiative to develop Al Widyan as the world's largest shopping and entertainment destination, you were building a new shopping mall complex. You would determine how many stores, staff, and customers would need to be accommodated, where precisely to locate the site, and assess transport links. You might consider a few styles of buildings. You would draw designs and build at least one model to make sure the layout was suitable for all needs. Finally, after creating schedules and enlisting help from experts, you would dig the first foundations. All of these activities involve analyz- ing, evaluating, and making objective decisions to make sure the result is sound and successful. The same is true for critical thinking. In this chapter, you explore what it means to think critically and how to become a critical thinker. case At the travel company, you have been working with Omar, the vice president of finance, to solve the problem of declining sales. Your project team is now track- ing the progress of the solution: increasing the enrollment of the company's most popular tours. These tours include trips to Dammam, Abha, and Ha'il. So far, the enrollment for the Abha and Ha'il tours have improved steadily. In fact, the Al-Qishlah Palace tour in Ha'il is now one of the top five all-time best sellers. However, sales for the active tours in Dammam remain flat, despite the region's popularity. Omar asks you to help him determine the reasons for the flat sales. LEARNING OBJECTIVES Once you have completed this chapter, you should be able to: 1 Understand critical thinking 2 Overcome obstacles to critical thinking 3 Become a critical thinker وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 Business Decision Making S1 S2 S3.indb 73 Thinking Critically 73 30/06/2023 14:28

Thinking Critically
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Once you have completed this chapter, you should be able to
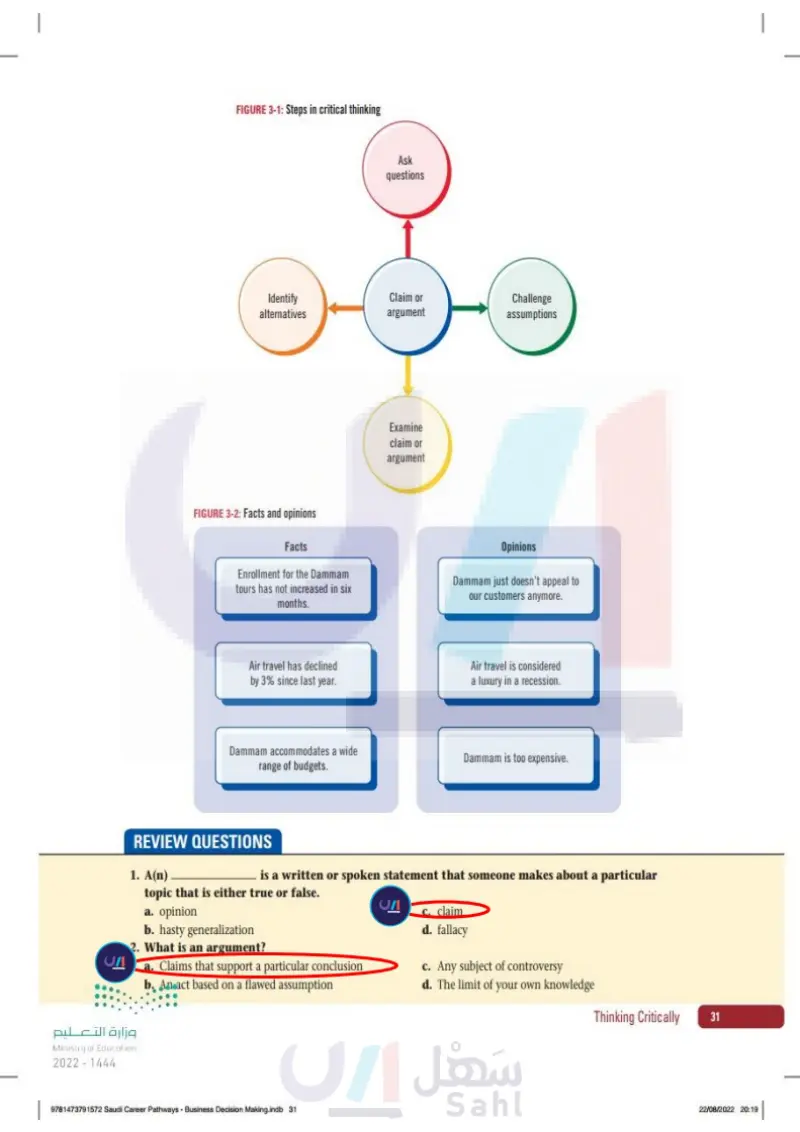
Lesson 1 Chapter 3 www.ien.edu.sa Understanding Critical Thinking One characteristic that differentiates humans from other animal species is the ability to think, reason, and make informed judgments about observations and facts. Thought and thinking are natural, sometimes automatic mental processes that include reasoning, remembering, imagining, and reflecting, for example. Critical thinking generally requires more analysis, evaluation, discipline, and rigor. The goal of critical thinking is often to improve choices and reduce the risk of adopting or acting on a flawed assumption. case Omar says that investigat- ing the reasons for the flat sales of Dammam tours requires critical thinking. He advises you to learn more about critical thinking to help him solve the sales problem. 74 Chapter 3 Ministry of Education 2024-1446 95198_book_PP1.indb 74 DEFINITION Critical thinking: The thoughtful, deliberate process of deciding whether you should accept, reject, or reserve judgment about a particular idea. The goal of critical thinking is often to improve choices and reduce the risk of adopting or acting on a flawed assumption. Details Ask yourself the following questions as you prepare to improve your critical thinking: What is critical thinking? Critical thinking is the thoughtful, deliberate process of deciding whether you should accept, reject, or reserve judgment about a particular idea. It is also a measure of your confidence in the idea itself. Use critical thinking whenever you make a decision, solve a problem, take an action, or decide what to believe. Although the word critical can mean to find fault or to criti- cize, critical thinking is not a negative activity. Rather, it is a process where you ask questions, challenge assumptions, examine claims, and identify alternatives or answers. See Figure 3-1. 07/05/2024 10:57

Understanding Critical Thinking
What is critical thinking?
وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 Business Decision Making S1 S2 S3.indb 75 FIGURE 3-1: Steps in critical thinking Identify alternatives Ask questions Claim or argument Challenge assumptions Examine claim or argument What is a claim? A claim is a statement that someone says or writes about a topic. The claim can be true or false. Many statements are not claims. For example, when you greet someone or ask a question, the statements are generally not either true or false. In contrast, you can measure the amount of truth in a claim. For example, if a colleague claims that the company tours to Dammam are the most popular, you can refer to tour sales to determine if that claim is true. When you are presented with a claim, you decide whether to accept, reject, or investigate it. DEFINITION Claim: A statement that someone says or writes about a topic. What is an issue? When you are solving problems or engaged in other activities that demand critical thinking, you are examining and thinking about an issue. In general terms, an issue is any controversial subject that you discuss, dispute, or review. An issue is different from a simple topic of conversation because it raises questions or concerns. For example, the Dammam tours at the travel Thinking Critically 75 30/06/2023 14:28

Steps in critical thinking
What is a claim?
What is an issue?
company are an issue-their sales should be increasing, but they are not, which raises concerns about the tours. DEFINITION Issue: Any challenging subject that you discuss, dispute, or review. An issue is different from a simple topic of conversation because it raises questions or concerns. . What is an argument? In common usage, argument means a heated discussion between people. In the context of critical thinking, an argument is a set of one or more claims that support a particular conclusion. The claims are sometimes called prem- ises. When you try to persuade someone to adopt your point of view, you typically make an argument and offer evidence that helps prove your claim as true. You should also evaluate other peoples' claims carefully and decide whether you accept their arguments. DEFINITION Argument: (1) A set of one or more claims that supports a particular conclusion. (2) A value or cell reference that a function uses in its calculations. . What is the difference between facts, opinions and factual matter? Thinking critically demands that you distinguish between fact and opinion. Typically, a fact is a claim that is considered to be true. An opinion is a claim that someone believes is true. Opinions may or may not be factual, even though people often assert their opinions as facts. Figure 3-2 compares facts and opinions. If you can collect data about and analyze a claim, it is said to be a factual matter. This term suggests that you are not certain the claim is a fact, but could prove or disprove if necessary. 76 Chapter 3 Ministry of Education 2024-1446 DEFINITIONS Fact: A claim that is considered to be true. Opinion: A claim that someone believes is true. Factual matter: A claim about which you can collect and analyze data. This term suggests that you are not certain the claim is a fact, but could prove or disprove if necessary. Business Decision Making S1 S2 S3.indb 76 30/06/2023 14:28

company are an issue their sales should be increasing, but they are not, which raises concerns about the tours
What is an argument?
What is the difference between facts, opinions and factual matter?
FIGURE 3-2: Facts and opinions Facts Enrollment for the Dammam tours has not increased in six months. Opinions Dammam just doesn't appeal to our customers anymore. Air travel has declined by 3% since last year. Air travel is considered a luxury in a recession. Dammam accommodates a wide range of budgets. Dammam is too expensive. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. A(n) is a written or spoken statement that some- one makes about a particular topic that is either true or false. a. opinion b. hasty generalization c. claim d. fallacy 2. What is an argument? a. Claims that support a particular conclusion b. An act based on a flawed assumption c. Any subject of controversy d. The limit of your own knowledge وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 Business Decision Making S1 S2 S3.indb 77 Thinking Critically 77 30/06/2023 14:28

FIGURE 3-2: Facts and opinions
A(n) is a written or spoken statement that someone makes about a particular topic that is either true or false
What is an argument?