Using Convergent Thinking - Business Decision Making - ثاني ثانوي
Part 1
Chapter1: Identifying and Defining Problems
Chapter2: Solving the Problem
Chapter3: Thinking Critically
Chapter4: Group Decision Making and Problem Solving
Chapter5: Decision Support Tools
Chapter 6: Decision-Making Processes in Organizations
Chapter 7: Managing Teams to Support Decisions in Organizations
Chapter 8: Organizational Communication and Decision Making
Part 2
Chapter 9: Using Data to Support the Decision-making Process
Chapter 10: Decision Support System Fundamentals
Chapter 12: The Car Production Project
Chapter 13: The Ski Resort Project
Chapter 14: The Electric Car Project
Chapter 15: The Airline Project
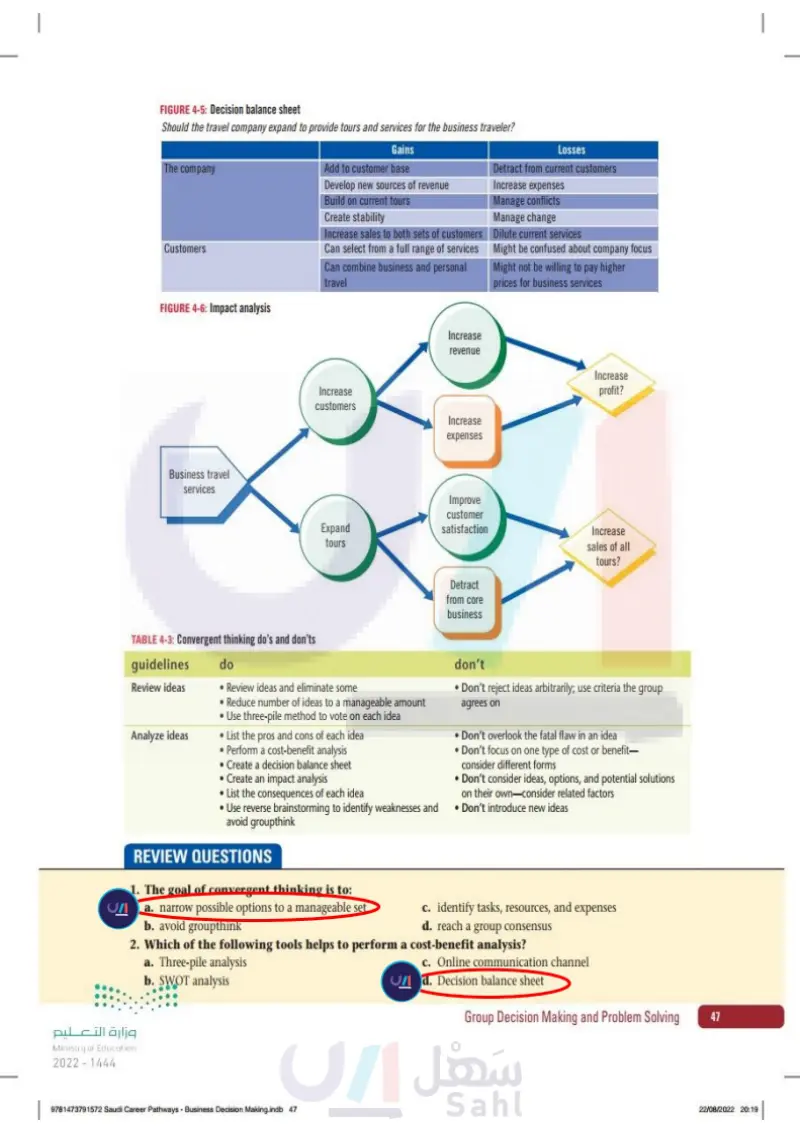
Lesson 4 Chapter 4 www.ien.edu.sa Using Convergent Thinking In the early stages of solving a problem, you use divergent thinking to develop as many creative ideas and potential solutions as possible. At some point, how- ever, the group needs to review and evaluate the ideas in an organized, under- standable, and structured format. Convergent thinking techniques narrow the options to a manageable set. The decisions and solutions that the group eventu- ally makes will be based on these organized ideas. Table 4-3 lists the do's and don'ts for convergent thinking. case Now that the corporate travel team met to generate ideas, Omar plans a meeting to organize and evaluate the ideas. He asks you to learn about techniques for structuring group ideas and solutions. DEFINITION Convergent thinking: Thought processes or methods that narrow options to a manageable set. TABLE 4-3: Convergent thinking do's and don'ts Guidelines Review ideas Analyze ideas Do • Review ideas and eliminate some Reduce number of ideas to a manageable amount • Use three-pile method to vote on each idea •List the pros and cons of each idea • Perform a cost-benefit analysis • Create a decision balance sheet • Create an impact analysis • List the consequences of each idea Don't • Don't reject ideas arbitrarily; use criteria the group agrees on • Don't overlook the fatal flaw in an idea • Don't focus on one type of cost or benefit― consider different forms • Don't consider ideas, options, and potential solutions on their own consider related factors • Use reverse brainstorming to identify weaknesses and Don't introduce new ideas avoid groupthink وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 95198_book_PP1.indb 105 Essential Elements 1. Review your ideas If your group's divergent thinking has gone well, you should have a sizable set of ideas, options, and possibilities to consider. One of the first tasks for the group is to carefully review these ideas and cull, or remove, the imprac- tical ones. A popular culling approach is the three-pile method. Review Group Decision Making and Problem Solving 105 07/05/2024 10:57

Using Convergent Thinking
Convergent thinking do’s and don’ts
Review your ideas
each option and have the group vote to put the idea into either a Yes, No, or Maybe pile (or category). A simple plurality of votes is needed for each. The No pile is eliminated from further consideration. The Maybe pile is held in reserve and may be revisited if necessary. DEFINITION Three-pile method: A technique for reducing ideas to a manageable number. QUICK TIP Identify pros and cons in an informal discussion, or more formally with someone recording the feedback for all to see. 2. Identify the pros and cons Have the group consider each option or idea one at a time and identify the associated pros and cons. The objective is to have the group consider each option in an objective manner. Ask the group if there is a fatal flaw inherent in any of the ideas. A fatal flaw is some aspect of an idea that would make it unacceptable. DEFINITION Fatal flaw: An aspect of an idea that would make it unacceptable for some reason. 3. Perform a cost-benefit analysis Each idea that is proposed will have some benefit to the group or organiza- tion. It will also have some associated costs. Good ideas typically have bene- fits that outweigh their costs. Costs and benefits may take different forms such as monetary return, cost savings, improved efficiency, reduced prob- lems, and others, and comparing one to another may be tricky. A decision balance sheet is a formal way of organizing an idea's costs and benefits. See Figure 4-5. FIGURE 4-5: Decision balance sheet Should the travel company expand to provide tours and services for the business traveler? The company Customers 106 4 Chapter رة ا Ministry of Education 2024-1446 Business Decision Making S1 S2 S3.indb 106 Gains Add to customer base Develop new sources of revenue Build on current tours Create stability Increase sales to both sets of customers Can select from a full range of services Can combine business and personal travel Losses Detract from current customers Increase expenses Manage conflicts Manage change Dilute current services Might be confused about company focus Might not be willing to pay higher prices for business services 30/06/2023 14:28

each option and have the group vote to put the idea into either a Yes
Identify the pros and cons
Perform a cost-benefit analysis
DEFINITION Decision balance sheet: A formal way of organizing an idea's costs and benefits. QUICK TIP An impact analysis alone should not drive the final decision, but can help to better differentiate between alternatives. 4. Create an impact analysis It is easy to consider ideas, options, and potential solutions by themselves and not consider other related factors. Use an impact analysis to broaden your view. Have the group list the consequences of each idea. Who or what would each option affect? Would the consequences be minimal or man- ageable? Which idea would cause the least amount of loss or harm? See Figure 4-6. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 DEFINITION Impact analysis: A way of evaluating the effects of an idea or alternative. FIGURE 4-6: Impact analysis Business travel services Business Decision Making S1 S2 S3.indb 107 Increase revenue Increase customers Increase profit? Increase expenses Expand tours Improve customer satisfaction Increase sales of all tours? Detract from core business 5. Use reverse brainstorming Brainstorming is usually thought of as a divergent thinking technique. However, when used in reverse it can be a helpful convergent tool. Present each idea or option to the group and ask everyone to identify possible weak- nesses or problems. The goal is not to come up with new ideas, but to gen- Group Decision Making and Problem Solving 107 30/06/2023 14:28

Decision balance sheet: A formal way of organizing an idea’s costs and benefits.
Create an impact analysis
Use reverse brainstorming
erate criticisms instead. This exercise forces people to take a hard look at each option and helps minimize problems associated with groupthink. The group can reexamine the ideas to generate possible solutions for each of the weaknesses identified. YOU TRY IT Practice using convergent thinking by generating solutions to a problem. Complete the following steps. 1. Get ready At the travel company you're working at, one idea generated during diver- gent thinking activities was to expand the company Web site to provide general services for business travelers. The Web site would let business trav- elers do the following: Find information about destinations. Request services from the travel company staff, such as group accom- modation, travel reservations, and event planning. • Look up information about flights, tours, excursions, and reservations. 2. Now you try it REVIEW QUESTIONS Use a convergent thinking technique to evaluate the problem of whether the company should expand its Web site to include services for business travelers. 1. The goal of convergent thinking is to: a. narrow possible options to a manageable set b. avoid groupthink c. identify tasks, resources, and expenses d. reach a group consensus 2. Which of the following tools helps to perform a cost-benefit analysis? a. Three-pile analysis b. SWOT analysis c. Online communication channel d. Decision balance sheet 108 4 Chapter رة ا Ministry of Education 2024-1446 Business Decision Making S1 S2 S3.indb 108 30/06/2023 14:28

erate criticisms instead. This exercise forces people
Practice using convergent thinking by generating solutions to a problem. Complete the following steps
Use a convergent thinking technique to evaluate the problem of whether the company should expand its Web site to include services for business travelers
The goal of convergent thinking is to
Which of the following tools helps to perform a cost-benefit analysis