Working with Data - Data Science - ثاني ثانوي
1. Introduction to Data Science
3. Exploratory Data Analysis
4. Predictive data modeling and forecasting
Lesson 2 Working with Data Link to digital lesson www.ien.edu.sa What is Big Data? The term "Big Data" refers to data that is either too large or too complex to process using typical methods. Due to the fact that this amount of data. is too large for typical computing systems to manage, the storing and the processing of these huge datasets is considered a challenge. Furthermore, data collection might be so rapid that storage requirements are extremely high. Big Data A large dataset that requires scalable technologies for storage, processing, management, and analysis due to its characteristics of volume, variety, velocity, veracity and value. Characteristics of Big Data There are five key concepts that help us to classify any data under the term of "Big Data": the Variety, the Value, the Volume, the Veracity and the Velocity. Data is considered "Big" when it comes in large volumes, at a very fast rate, with great Variety, and is accurate and useful. Data must fulfill all these "Vs" in order to be considered "Big Data". Variety Variety refers to the many different types of data that are available. Traditional data types were structured and fit neatly in a relational database. With the rise of big data, data comes in new unstructured data types. Unstructured and semistructured data types (such as text, audio, and video) require additional preprocessing to derive meaning and support metadata information. Without the metadata, it will be impossible to know what is stored and how it can be processed. Velocity Veracity وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 добо Variety יוון Volume Value Figure 1.6: The Big Data characteristics - The 5 Vs 21

Characteristics of Big Data
What is Big Data?
Big Data
Variety
Value Just because we collected lots of data, this does not mean it is of any value, we have to garner some insights out of it. Value refers to how useful the data is in decision making. We need to extract the value of the big data using appropriate analytics. Veracity Data veracity has to do with how accurate or truthful a dataset may be. It's not just the quality of the data itself but how trustworthy the data source, type, and processing is. Volume Because large volumes of low-density, unstructured data must be handled, the amount of data is a critical aspect in big data. This can be unvalued data like clickstreams on a website or mobile app, or sensor-enabled IoT devices. It might be tens of terabytes of data at times, and hundreds of petabytes at other times. Velocity The rate at which data is captured and stored is referred to as velocity. Most internet-connected smart devices (IoT devices) and mobile devices work in real-time or near real-time, requiring instant data collection, transmission and storage. Technologies that Enable the Management of Big Data Businesses use computer systems and databases to keep records of transactions such as order processing, payments, customer tracking, and cost management. Furthermore, a company will require a reporting system to provide information that will help it run more efficiently and help executives make more informed and, hopefully, better decisions. Furthermore, an e-shop, for example, will need to enhance the buying experience and ensure that the website visitors become customers or that an existing customer will return to buy again. By analyzing all the data captured during the e-shop browsing on the web or through a mobile app, the company can find out where its visitors place their cursors, which parts of the website they stare at the most and how long they hover over a product before making a click for more information or an actual purchase. Tiny details are becoming a huge amount of data waiting to be analyzed and become valuable insights. This information will drive changes in the website's layout, price reductions or increases, and product campaigns on social media to influence buying behaviors. Companies require new technologies and tools to manage and analyze big data to extract business value. The required data must be gathered from internal sources such as sales, manufacturing, and accounting, and external sources such as demographic and competition data to extract concise, reliable information about the company's current state and market dynamics. Modern infrastructure for business intelligence has an array of tools to store and process data to obtain useful information from big data. These technologies include data warehouses, data lakes and in-memory computing. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 22 ZU24-1446

Value
Volume
Veracity
Velocity
Technologies that Enable the Management of Big Data
Data Warehouse As the most traditional tool to analyze corporate data, a data warehouse refers to the database that stores current and historical data originating from many core operational transaction systems (sales, customer support, manufacturing) and makes data available to a company's decision makers. This data is combined with data from external sources to transform incomplete data to structured data before being stored in the data warehouse. A data warehouse system also provides a range of ad hoc and standardized query analysis and graphical reporting tools. In-Memory Computing This is a way of facilitating big data analysis, because it relies primarily on the computer's main memory (RAM) for data storage. Users access data stored in system primary memory, thereby eliminating bottlenecks from retrieving and reading data that are present in a traditional, disk-based database and dramatically shortening query response times. Very large quantities of RAM on cloud servers facilitate this method. Data Lake A data lake is a repository, usually in the cloud, to store huge amounts of raw and unprocessed data. It uses a flat URL structure to support both structured data (such as databases) and unstructured data (such as emails and documents). The distinction between these three technologies is important because they serve different purposes and require different handling to be properly optimized. They do not work all together but, depending on the type of company, one of the three is chosen - a data lake may work well for one company, while a data warehouse will be a better fit for another. Mining Big Data Big data is being continuously collected by sensors and by applications in our environments and applications that we use personally. But collecting the data is only the first step in the process referred to as Knowledge Discovery. Knowledge discovery refers to the overall process of discovering useful knowledge from data, and data mining refers to a particular step in this process. Data mining is the application of specific algorithms for extracting patterns from data and identifying relationships. The additional steps in the knowledge discovery process, such as data cleansing, data integration, data transformation, and proper interpretation of the results of mining, are essential to ensure that useful knowledge is derived from the data (see Table 1.6). Some of the main tasks accomplished by data mining are: Analyzing data to discover patterns and trends. Formulating predictions for different dataset inputs. Classifying, clustering or forecasting the different values of the dataset. Facilitating decision recommendations. Data Mining Analysis of large pools of data to find patterns and rules that can be used to guide decision making and predict future behavior. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 23

Data Warehouse
In-Memory Computing
Data Lake
The distinction between these three technologies
Mining Big Data
Data Mining
Some of the main tasks accomplished by data mining are:
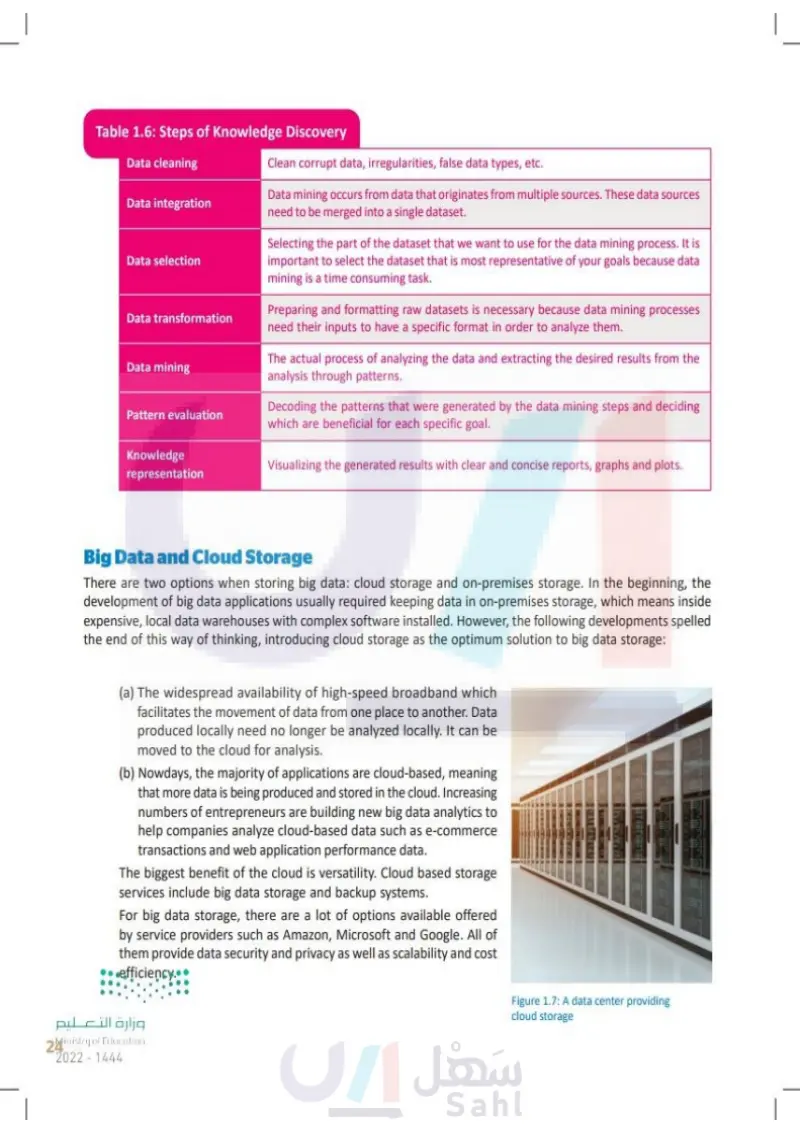
Table 1.6: Steps of Knowledge Discovery Data cleaning Data integration Data selection Data transformation Data mining Pattern evaluation Knowledge representation Clean corrupt data, irregularities, false data types, etc. Data mining uses data that originates from multiple sources. These data sources need to be merged into a single dataset. Selecting the part of the dataset that we want to use for the data mining process. It is important to select the dataset that is most representative of your goals because data mining is a time consuming task. Preparing and formatting raw datasets is necessary because data mining processes need their inputs to have a specific format in order to analyze them. The actual process of analyzing the data and extracting the desired results from the analysis through patterns. Decoding the patterns that were generated by the data mining steps and deciding which are beneficial for each specific goal. Visualizing the generated results with clear and concise reports, graphs and plots. Big Data and Cloud Storage There are two options when storing big data: cloud storage and on-premises storage. In the beginning, the development of big data applications usually required keeping data in on-premises storage, which means inside expensive, local data warehouses with complex software installed. However, the following developments spelled the end of this way of thinking, introducing cloud storage as the optimum solution to big data storage: (a) The widespread availability of high-speed broadband which facilitates the movement of data from one place to another. Data produced locally need no longer be analyzed locally. It can be moved to the cloud for analysis. (b) Nowdays, the majority of applications are cloud-based, meaning that more data is being produced and stored in the cloud. Increasing numbers of entrepreneurs are building new big data analytics to help companies analyze cloud-based data such as e-commerce transactions and web application performance data. The biggest benefit of the cloud is versatility. Cloud based storage services include big data storage and backup systems. For big data storage, there are a lot of options available offered by service providers such as Amazon, Microsoft and Google. All of them provide data security and privacy as well as scalability and cost efficiency. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 24 2024-1446 Figure 1.7: A data center providing cloud storage

Steps of Knowledge Discovery
Big Data and Cloud Storage
By using cloud backup for big data, enterprises can utilize services from data centers that span multiple geographic locations, ensuring high availability and easy data recovery. Using the cloud, backed up data can be replicated over multiple data centers in different regions of the world. This way, the backups aren't kept at a single location. There is another layer of security to the backup. Service providers ensure that the data being backed up to the cloud is protected via advanced encryption techniques before, after and during transit. As mentioned earlier, big data handling requires storage capacity and processing power. In terms of storage capacity, the cloud fulfills this role. Enterprises can acquire storage services that facilitate simplified scalability. And these services are also capable of meeting the computation requirements of big data. Actually, experts recommend cloud powered data analytics for big data analysis based on the almost infinite computing capabilities of the cloud. Pros and Cons of Big Data Cloud Storage The combination of big data analytics and cloud computing can generate opportunities that were not feasible previously. But apart from the advantages, the data scientist needs to be aware of the challenges. Table 1.7: Big data cloud storage advantages and disadvantages Advantages Large volumes of structured and unstructured data require increased transmission bandwidth and storage. The cloud provides readily-available infrastructure and the ability to scale up to handle any amount of data traffic and storage requirements. Disadvantages Less direct control over data security. Data breaches could lead to serious penalties under the latest data privacy regulations. Storing big data in the cloud eliminates the need to maintain expensive on-premises hardware, software and specialized staff. The pay-as-you-go cloud computing model is more cost-efficient, reducing the waste of resources. The cloud service provider can raise the rates of their cloud infrastructure anytime. The company that consumes these services may become locked in a business relationship that is not cost-efficient. The company focuses on the analytics process rather than the infrastructure management, impacting positively on the business's culture, performance, and competitive advantage. Storing big data in the cloud means data. availability depends on network connectivity. Also, the issue of latency in the cloud environment spills over into the speed of capturing, processing and storing data. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 25

By using cloud backup for big data,
Pros and Cons of Big Data Cloud Storage
Big data cloud storage advantages and disadvantages
Data Governance and Policies The policies, processes, and organizational structures define the decision rights and accountabilities to support data management. Data governance includes internal policies and procedures controlling the management of data. Data governance assists private enterprises or state and non-profit organizations in working with high-quality data management processes through all data life cycle phases. These effective policies and procedures lead to improved business or organizational outcomes. Enterprises and organizations currently collect vast amounts of internal and external data, and data governance is necessary to use that data effectively, manage risks, and reduce costs. Data governance ensures that data is: Secure Trustworthy Documented Managed Audited The Importance of Data Governance Data inconsistencies in various systems within an organization may not be resolved without proper data governance. In sales and customer service systems, for example, customer names may be listed differently. This could make data integration more challenging and affect the accuracy of business intelligence and reporting. Furthermore, data errors may not be detected and corrected, compromising the integrity of data. More importantly, organizations that must comply with new data privacy and protection legislation, such as the European Union's GDPR and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), may encounter difficulties or even penalties as a result of poor data governance. In the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the new Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL) regulates the processing of personal data. The PDPL is the first state data privacy legislation in Saudi Arabia covering all industries and types of organizations. The National Data Management Office (NDMO) supervises and enforces the new regulations. The PDPL also applies to foreign organizations operating in Saudi Arabia and processing the personal data of Saudi residents, especially regarding genetic, health, credit and financial data. There are special types of data, such as financial or health data, that require careful handling. Health data is usually well governed from the time of data collection up to reporting and dissemination of information. All stakeholders fully understand the privacy risk and the constraints set by legislation, therefore a well-defined data governance framework, in a hospital, for example, is valuable. Data Governance Framework Components The policies, guidelines, processes, organizational structures, and technology implemented as part of a governance program make up a data governance framework. The framework also specifies the program's mission, goals, how success will be measured, and accountability for the functions that will be included in the program. The governance framework of an organization should be established ●⚫and disseminated internally to explain how the program will work so that everyone engaged has a clear understanding from the start. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 26 ZU24-1446

Data Governance and Policies
Data governance ensures that data is:
The Importance of Data Governance
There are special types of data, such as financial or health data,
Data Governance Framework Components
Data Governance Standards ISO, the International Standards Organization, has developed a standard, ISO/IEC 38505, to apply IT governance principles to the data governance requirements. Table 1.8: The six data governance principles Assign to personnel Align with the mission and vision of the organization Responsibility Strategy Acquisition Align with the organizational requirements Conformance Performance Human behavior Ensure compliance with legislation, internal policies and business ethics Meet the requirements of the organization Encourage people to get involved Saudi Data Management Standards Similar to the ISO/IEC 38505 data governance requirements, the National Data Management Office (NDMO) developed the National Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standards. The NDMO is responsible for implementing the standards and policies, governance mechanisms and controls for data and artificial intelligence, and monitoring compliance by organizations and companies. The standards apply to all data regardless of form or type, including paper records, digital data, voice recordings, photos, videos, handwritten documents, or any other recorded data. https://sdaia.gov.sa/ndmo NDMO National Data Management Office Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standards Figure 1.8: Sample pages from the NDMO Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standards. O Saudi Data & Al Authority Example A Saudi telecom company created its corporate analytics and data division to help meet its objective of introducing data governance and management best practices. The company's pillars of data governance are people, processes and technologies, with the initiative addressing all pillars for a successful digital transformation. The company now seeks to adopt innovative data governance solutions that leverage artificial intelligence and extend the data governance concept to "analytics governance". The goal is to achieve positive business change through well-defined data workflows and requirements. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 27

Data Governance Standards
The six data governance principles
Saudi Data Management Standards
Sample pages from the NDMO Data Management and Personal Data Protection Standards. © Saudi Data & Al Authority
A Saudi telecom company created its corporate analytics and data division to help meet its objective of introducing data governance and management best practices.
Data Governance and Data Management It is critical to recognize that data governance is a component of overall data management. Data governance without actual implementation is just paperwork. Data governance establishes all policies and processes, whereas data management implements them to compile data and use it for decision-making. To draw an analogy, data governance is designing the plan of a new building, whereas data management is the act of building it. Furthermore, while you could build a house without a plan, it would be less efficient and effective, with a high risk of structural failures. Data management Data management is the creation and implementation of architectures, policies, and procedures that manage an organization's full data life cycle needs. Data Governance Challenges Cloud data and big data are two common data governance concerns that organizations encounter. Cloud services and big data systems introduce new governance requirements. Traditionally, data governance programs have focused on structured data stored in the data center. They now have to cope with the usual mix of structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data seen in big data environments, as well as the privacy threats associated with cloud data platforms. Who is Responsible for Data Governance? The data governance process involves a variety of people in most organizations. End-users familiar with relevant data in an organization's systems are included, as are business executives, data management specialists, and IT personnel. The key persons are the Chief Information Officer (CIO) or Chief Data Officer (CDO) and the Data Governance Manager (DGM). The CIO is usually a senior executive in charge of the data governance program. The CIO's responsibilities include obtaining approval, funding and staffing for the program, taking the lead in its establishment, evaluating its development, and acting as its internal advocate. Depending on the organization's size, a dedicated DGM may be appointed to lead and coordinate the process, hold meetings and training sessions, track KPIs (key performance indicators), and manage internal communications for the initiative. The DGM works with data owners and data stewards who ensure that the data governance policies and rules are enforced, and that end-users follow them. Data Owner An individual or people who are accountable for particular data. Data Steward A data management role that includes implementing and maintaining data governance policies within an organization. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 28 ZU24-1446

Data Governance versus Data Management
Data management
Data Governance Challenges
Who is Responsible?
Data Owner
Data Steward
Exercises 1 Read the sentences and tick ✓ True or False. 1. Big data refers to data that is either too large or too complex to process using typical methods. 2. Some of the five technologies that enable the management of big data are the Velocity, the Veracity and the Data Warehouse. 3. Knowledge discovery is a simple process that doesn't require any specific steps. 4. Cloud storage is the only storage method provided for the large amounts of data required for big data applications. 5. Faster scalability and lower cost of analytics are some of the many advantages of big data cloud storage. 6. A data warehouse is a repository, usually in the cloud, to store huge amounts of raw and unprocessed data. 7. In-memory computing is a way of facilitating big data analysis, because it relies primarily on the computer's main memory (RAM) for data storage. 8. A data lake refers to the database that stores current and historical data originated from many core operational transaction systems. 9. Data selection involves selecting the part of the dataset that we want to use for the knowledge discovery process. 10. Knowledge representation is the process of extracting the data from the analysis through patterns. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 True False 29

Read the sentences and tick True or False. Big data refers to data that is either too large or too complex to process using typical methods
2 Give three examples of how big data can help businesses. 3 Search the internet in order to find today's most popular cloud computing service providers in the global market, which are used to store and process big data. 4 Explain in a few sentences how the cloud helps us deal with the problem of storing the huge amount of data that big data represents. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 30 2024 -1446

Give three examples of how big data can help businesses.
Search the internet in order to find today's most popular cloud computing service providers in the global market, which are used to store and process big data.
Explain in a few sentences how the cloud helps us deal with the problem of storing the huge amount of data that big data represents.
5 Big data is a recent development in the history of computing. Can you identify two factors that enabled this sudden growth of data collection? 6 Compare the three big data storage technologies. If you developed an application that requires very fast access to data, which one would you choose? 7 Why is pattern evaluation important for data mining? وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 31

Why is pattern evaluation important for data mining?
Compare the three big data storage technologies. If you developed an application that requires very fast access to data, which one would you choose?
Big data is a recent development in the history of computing. Can you identify two factors that enabled this sudden growth of data collection?
8 Explain how scalability works in cloud data storage. Find two cloud data storage services on the internet. 9 What is the purpose of data governance? Is data governance a synonym of data management? 10 Search on the internet for information about the health data management regulations or laws in Saudi Arabia. What would be the consequences of a data leak from a health care facility? وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 32 2024-1446

Explain how scalability works in cloud data storage. Find two cloud data storage services on the internet.
What is the purpose of data governance? Is data governance a synonym of data management?
Search on the internet for information about the health data management regulations or laws in Saudi Arabia. What would be the consequences of a data leak from a health care facility?
11 You are creating a report on climate change by comparing historical weather data of two countries. Where will you search for information on the internet? Explain the factors behind your decision. 12 What privacy concerns can you think of when a big enterprise organization deals with big data? 13 Can you think of how much a social network you have joined knows about your family and friends? Provide a short list of information. وزارة التعليم Ministry of Education 2024-1446 33

You are creating a report on climate change by comparing historical weather data of two countries. Where will you search for information on the internet? Explain the factors behind your decis
What privacy concerns can you think of when a big enterprise organization deals with big data?
Can you think of how much a social network you have joined knows about your family and friends? Provide a short list of information.